hidimstat.LOCO#
- class hidimstat.LOCO(estimator, loss: callable = <function root_mean_squared_error>, method: str = 'predict', n_jobs: int = 1)[source]#
Bases:
BasePerturbation- __init__(estimator, loss: callable = <function root_mean_squared_error>, method: str = 'predict', n_jobs: int = 1)[source]#
Leave-One-Covariate-Out (LOCO) as presented in Lei et al.[1] and Verdinelli and Wasserman[2]. The model is re-fitted for each variable/group of variables. The importance is then computed as the difference between the loss of the full model and the loss of the model without the variable/group.
- Parameters:
- estimatorsklearn compatible estimator, optional
The estimator to use for the prediction.
- losscallable, default=root_mean_squared_error
The loss function to use when comparing the perturbed model to the full model.
- methodstr, default=”predict”
The method to use for the prediction. This determines the predictions passed to the loss function. Supported methods are “predict”, “predict_proba” or “decision_function”.
- n_jobsint, default=1
The number of jobs to run in parallel. Parallelization is done over the variables or groups of variables.
Notes
Williamson et al.[3] also presented a LOCO method with an additional data splitting strategy.
References
- fit(X, y, groups=None)[source]#
Fit a model after removing each covariate/group of covariates.
- Parameters:
- Xarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
The training input samples.
- yarray-like of shape (n_samples,)
The target values.
- groupsdict, default=None
A dictionary where the keys are the group names and the values are the indices of the covariates in each group.
- Returns:
- selfobject
Returns the instance itself.
- get_metadata_routing()[source]#
Get metadata routing of this object.
Please check User Guide on how the routing mechanism works.
- Returns:
- routingMetadataRequest
A
MetadataRequestencapsulating routing information.
- get_params(deep=True)[source]#
Get parameters for this estimator.
- Parameters:
- deepbool, default=True
If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators.
- Returns:
- paramsdict
Parameter names mapped to their values.
- importance(X, y)[source]#
Compute the importance scores for each group of covariates.
- Parameters:
- X: array-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
The input samples.
- y: array-like of shape (n_samples,)
The target values.
- Returns:
- out_dict: dict
A dictionary containing the following keys: - ‘loss_reference’: the loss of the model with the original data. - ‘loss’: a dictionary containing the loss of the perturbed model for each group. - ‘importance’: the importance scores for each group.
- plot_importance(ax=None, ascending=False, **seaborn_barplot_kwargs)[source]#
Plot feature importances as a horizontal bar plot.
- Parameters:
- axmatplotlib.axes.Axes or None, (default=None)
Axes object to draw the plot onto, otherwise uses the current Axes.
- ascending: bool, default=False
Whether to sort features by ascending importance.
- **seaborn_barplot_kwargsadditional keyword arguments
Additional arguments passed to seaborn.barplot. https://seaborn.pydata.org/generated/seaborn.barplot.html
- Returns:
- axmatplotlib.axes.Axes
The Axes object with the plot.
- predict(X)[source]#
Compute the predictions after perturbation of the data for each group of variables.
- Parameters:
- X: array-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
The input samples.
- Returns:
- out: array-like of shape (n_groups, n_permutations, n_samples)
The predictions after perturbation of the data for each group of variables.
- selection(k_best=None, percentile=None, threshold=None, threshold_pvalue=None)[source]#
Selects features based on variable importance. In case several arguments are different from None, the returned selection is the conjunction of all of them.
- Parameters:
- k_bestint, optional, default=None
Selects the top k features based on importance scores.
- percentilefloat, optional, default=None
Selects features based on a specified percentile of importance scores.
- thresholdfloat, optional, default=None
Selects features with importance scores above the specified threshold.
- threshold_pvaluefloat, optional, default=None
Selects features with p-values below the specified threshold.
- Returns:
- selectionarray-like of shape (n_features,)
Binary array indicating the selected features.
- set_fit_request(*, groups: bool | None | str = '$UNCHANGED$') LOCO[source]#
Configure whether metadata should be requested to be passed to the
fitmethod.Note that this method is only relevant when this estimator is used as a sub-estimator within a meta-estimator and metadata routing is enabled with
enable_metadata_routing=True(seesklearn.set_config()). Please check the User Guide on how the routing mechanism works.The options for each parameter are:
True: metadata is requested, and passed tofitif provided. The request is ignored if metadata is not provided.False: metadata is not requested and the meta-estimator will not pass it tofit.None: metadata is not requested, and the meta-estimator will raise an error if the user provides it.str: metadata should be passed to the meta-estimator with this given alias instead of the original name.
The default (
sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED) retains the existing request. This allows you to change the request for some parameters and not others.Added in version 1.3.
- Parameters:
- groupsstr, True, False, or None, default=sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED
Metadata routing for
groupsparameter infit.
- Returns:
- selfobject
The updated object.
- set_params(**params)[source]#
Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as
Pipeline). The latter have parameters of the form<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.- Parameters:
- **paramsdict
Estimator parameters.
- Returns:
- selfestimator instance
Estimator instance.
Examples using hidimstat.LOCO#
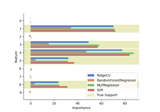
Leave-One-Covariate-Out (LOCO) feature importance with different regression models